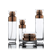- Material: Glass Products
- MOQ: 1pcs
- Volume: 60ml/75ml/100ml/120ml/150ml/200ml/250ml/300ml
- Sample: Avialable
- Feature: High Qiality
- Logo: Acceptable Customer’s Logo
-
Product nameAmber Glass Medical Screw-Top Packer Bottles Wide Mouth Container Jars for TabletProduct MaterialGlassVolume&Size50ml 60ml 75ml 100ml 120ml 150ml 200ml 250ml 300mlMOQ1pcsDelivery Port/Delivery Timein stock
Amber glass:
This entry is reviewed by the “Science China” Science Encyclopedia entry compilation and application work project.
Glass colored with sulfur-iron can be golden-brown-yellow-brown-red. At high temperatures, sulfur combines with the iron in the glass to form iron sulfide, and then combines with polysulfides to form thioferrite, which makes the glass brownish-red, which is often called amber.
Factors affecting the coloring of amber glass:
Control of glass composition
The content of silicon and aluminum in the glass formulation (SiO2+AI2O3) should not be too high, generally controlled below 73%, and the content of soda-calcium [Na2O(K2O)+CaO] should not be too low, generally controlled above 25%. Otherwise, it is not easy to melt and produce silicic acid thin skin. Because of the sulfate formed in the thin silicic acid skin and the accompanying reaction of sulfate and sulfite, this is the cause of secondary bubbles. When the barrel and the punch are slightly deviated, the bubbles will be brought into the glass product. In addition, appropriate amounts of manganese, copper, and titanium can be added to the glass formulation. These oxides all contribute to the purity and stability of the amber color.
Influence of melting atmosphere
The sulfur from the sulfide reacts with iron to form a chromophore. This combination is a weak chemical combination, which is susceptible to oxidation to form elemental sulfur or sulfate. The color tone will change with the change of the melting atmosphere. If the oxidizing atmosphere is too high, the FeS in the glass is easily oxidized to FeO, which affects the color of the glass and causes the color tone to be unstable. On the contrary, if the reducing atmosphere is too strong, although it has little effect on the color tone of the glass, it will affect the melting quality of the glass (that is, the generation of bubbles).
The influence of iron content in glass
The iron content plays an important role in the coloring of amber glass. Because if the glass contains no iron at all, it will be colorless even with the addition of sulfate and carbon powder. Therefore, the content of iron in the glass should be appropriate, too high to form iron sulfide, the color of the glass changes from brown to gray to grayish brown: on the contrary, the amber color of the glass is very unstable and will produce bubbles if it is too low. Therefore, the iron content in the glass is generally controlled at about 0.2%.
The effect of manganese in glass on amber
Everyone knows that when manganese and iron are introduced into glass, they can be colored amber by themselves. The presence of manganese in the sulfur-carbon colored glass can increase the concentration of Fe and greatly reduce the influence of the melting atmosphere and the color change of Fe. This is because when two redox substances of manganese and iron exist in the glass at the same time, due to their interaction, manganese can oxidize the iron in the glass, and the manganese itself is also reduced. Hence the addition of MnO2. It can make the color of amber glass more pure, the coloring more stable, and the degree of color change is also small. At the same time, the 02 produced by the decomposition of MnO2 at high temperature can also play a clarifying role, which is beneficial to the elimination of small bubbles such as S02.
2FeO+2MnO2=Fe2O3+Mn2O3
Influence of reducing agent in glass
The carbon powder added to the amber glass does not have a coloring effect, but is introduced as a reducing agent. Generally in amber glass. Coke is often used as a reducing agent. Because the use of coke has the following advantages:
1) Coke has high carbon content and high flash point, so it will not lose its reducing effect due to burning too fast.
2) The coke has less impurities and will not affect the actual weight.
3) The particle size of coke is easy to control. Generally, it is better to control it at 1 fold. If it is too large, the reduction rate will be low; on the contrary, it should not be too small. And affect the color of amber glass.
4) The iron content of coke is low, thereby reducing the gray-brown generation in amber glass.
5) Coke is suitable for the formulation of low-alkali and high-calcium glass (such as the production of amber beer bottles) to form a good amber white glass. When coke is used as a reducing agent in amber glass, the moisture content of coke should also be controlled at 0.4-0.5%. The amount of coke introduced should not be too high. Otherwise, bubbles will be generated. The introduction of coke can also prevent the oxidation of sulfur.
The effect of fining agent in glass
In principle, no oxidizing agent is used in amber glass, otherwise it will affect the color change of amber glass. Commonly used clarifiers in amber glass are sulfate (Na2SO4) and table salt (NaCl). When the sulfate is reduced to sulfide under the action of the reducing agent, SO2 gas is released, which plays a clarifying role in the glass. However, when the sulfide is reduced to form a coloring group with iron at high temperature, it can also react with sulfate to form secondary bubbles. Brings difficulties to the clarification of the glass. Therefore, in order to reduce the formation of ash bubbles, the amount of sulfate introduced should not be too much. The amount of sulfate introduced in 100 kg of quartz sand is within the range of 0.5-2 kg, and the amount of salt introduced is preferably 2 to 3 kg.
Preparation:
Raw material preparation
Weigh out quartz sand, aluminum hydroxide, calcite, dolomite, soda ash, potassium carbonate, barium sulfate, iron oxide and sulfur oxide according to the weight of the raw materials, and mix them evenly;
High temperature melting
Melting at a high temperature in an oxidizing atmosphere at a melting temperature of 1450-1500°C, and adding carbon powder 1-3;
Forming processing
As the temperature of the molten liquid decreases to 1000-1200°C, the viscosity increases, and then the molding process is carried out;
annealing
Control the annealing temperature and atmosphere, the softening temperature is 744℃, and the annealing temperature is 568℃.


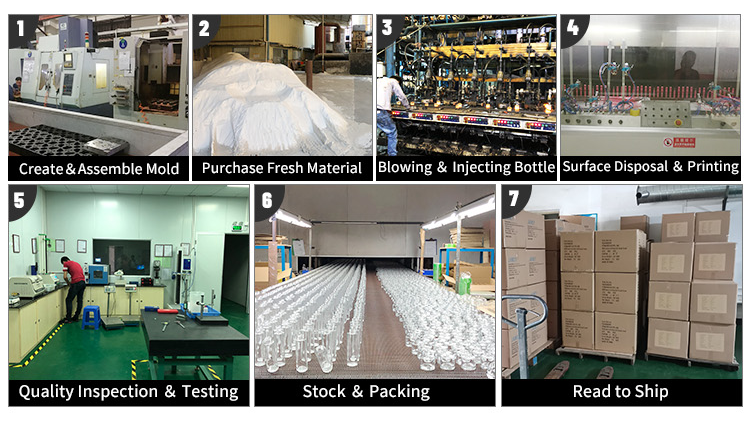
Production Process
Why Choose Us